How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to efficient surveying. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of everything you need to know, from pre-flight checks and understanding your drone’s controls to mastering advanced techniques and ensuring safe operation. We’ll cover essential safety procedures, navigation strategies, camera operation, and maintenance tips, equipping you with the knowledge to confidently take to the skies.
This detailed walkthrough will demystify the process, making drone operation accessible to beginners while offering valuable insights for experienced pilots looking to refine their skills. We’ll explore various flight modes, camera settings, and troubleshooting techniques, ensuring you’re prepared for any situation. By the end, you’ll possess the confidence and expertise to capture stunning visuals and enjoy the thrill of flight responsibly.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting various components and understanding relevant regulations. Failure to do so can lead to accidents and legal issues.
Drone Pre-Flight Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection helps identify potential problems before they lead to flight issues. This should be a routine before every flight.
| Component | Inspection Item | Acceptable Condition | Unacceptable Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Visual inspection for cracks, damage, or imbalance | No cracks, damage, or significant imbalance; securely fastened | Cracks, chips, significant bending, loose fasteners |
| Battery | Check voltage and charge level | Sufficient charge for intended flight time; no visible damage or swelling | Low charge, visible damage (swelling, cracks), loose connections |
| Camera | Lens clarity and gimbal function | Lens clean and clear; gimbal moves smoothly and accurately | Dirty or scratched lens; gimbal jerky or unresponsive |
| Airframe | Check for any damage or loose parts | No visible damage; all parts securely attached | Cracks, broken parts, loose screws or components |
Understanding Local Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
Operating a drone requires adherence to local laws and airspace regulations. These vary by location and can include restrictions on flight altitude, proximity to airports, and permitted flight zones. Ignoring these regulations can lead to hefty fines and legal repercussions.
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a good grasp of regulations and safety procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering all these essential elements, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone which will help you get started. Ultimately, safe and effective drone operation is a skill honed through practice and a thorough understanding of the technology.
Safe Drone Launch Procedures
Launching a drone safely involves a methodical approach. This minimizes the risk of accidents and ensures a smooth takeoff.
- Power on the controller first, followed by the drone.
- Calibrate the compass and GPS (if applicable).
- Choose a safe, open area away from obstacles and people.
- Perform a pre-flight check of the drone’s systems.
- Slowly lift the drone into the air, maintaining a steady hand.
- Once airborne, gradually increase altitude.
Emergency Procedures
Being prepared for emergencies is crucial for safe drone operation. Knowing how to handle low battery warnings and signal loss is paramount.
- Low Battery: Immediately initiate a controlled descent and return to the launch point. Do not attempt complex maneuvers.
- Loss of Signal: Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If RTH fails, attempt to manually guide the drone back, but prioritize safety.
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Mastering drone controls is essential for safe and effective operation. Understanding the controller’s functions and various flight modes is crucial for navigating different environments.
Drone Controller Functions
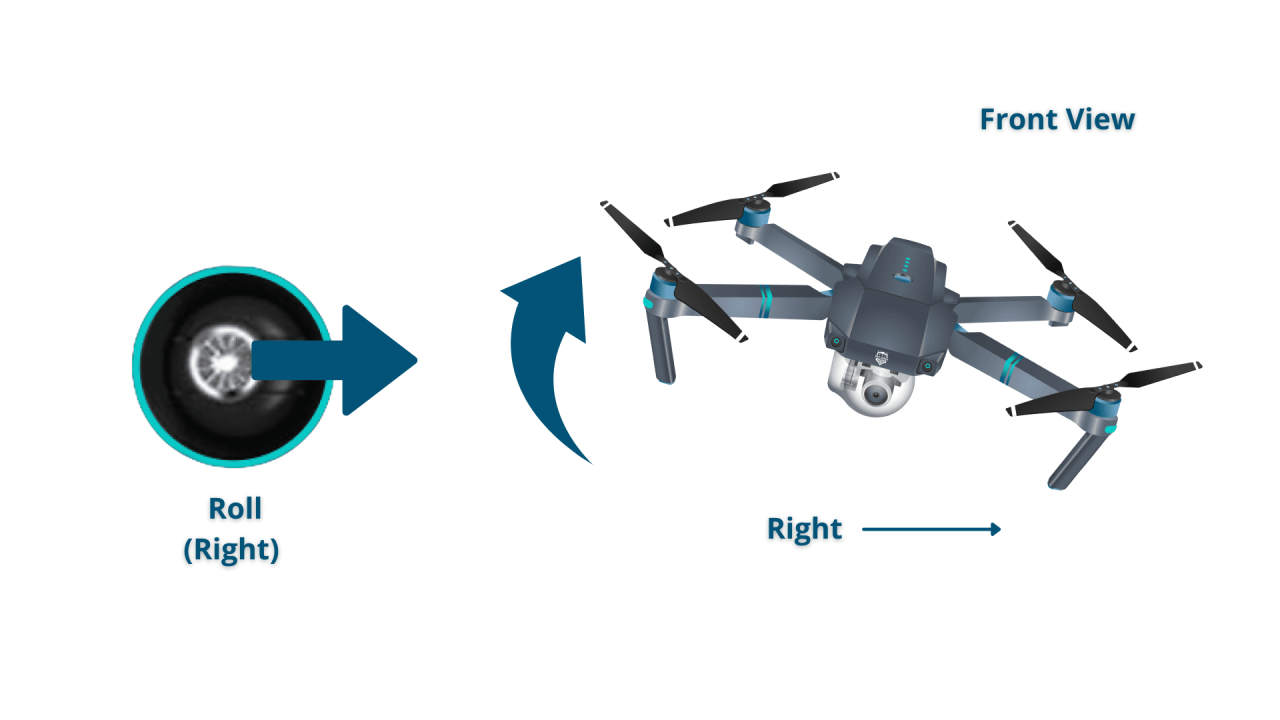
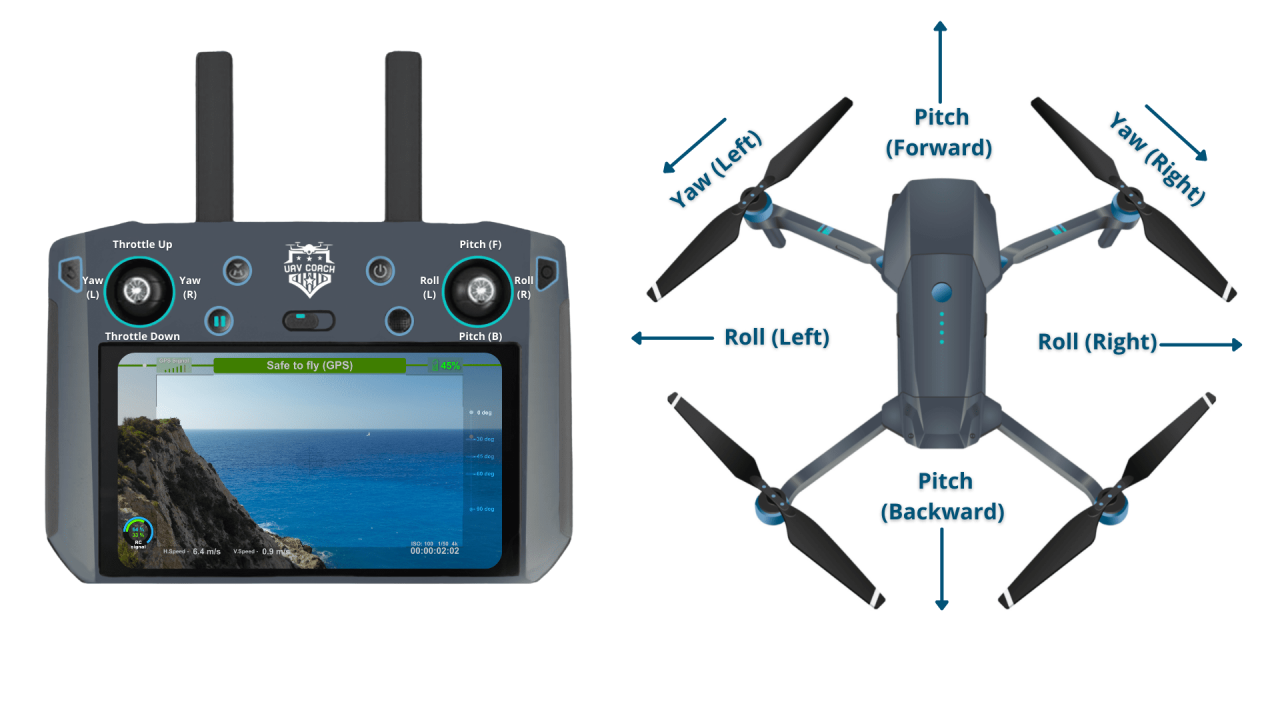
A standard drone controller typically has controls for throttle, yaw, pitch, and roll. Understanding their individual effects on the drone’s movement is critical.
- Throttle: Controls altitude (up and down).
- Yaw: Controls rotation around the drone’s vertical axis (left and right rotation).
- Pitch: Controls movement forward and backward.
- Roll: Controls movement left and right.
Drone Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability. Choosing the appropriate mode depends on the environment and pilot skill.
- GPS Mode: Maintains position and altitude using GPS signals; ideal for stable flight and easy control.
- Attitude Mode: Maintains orientation but not necessarily position; useful for precise maneuvers in stable environments.
- Manual Mode: Offers complete control but requires significant skill; not recommended for beginners.
Controller Inputs and Drone Movements
Imagine a three-dimensional coordinate system with the drone at its center. The controller inputs translate to movements along these axes. Throttle controls vertical movement (Z-axis), while pitch and roll control movement along the X and Y axes, respectively. Yaw rotates the drone around the Z-axis.
Navigating Drones in Various Environments
Navigating a drone safely requires awareness of the surrounding environment and adjusting flight techniques accordingly.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Successfully piloting a drone requires practice and knowledge, and a great resource to learn more is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. This will help you confidently handle your drone and ensure safe and responsible operation.
- Open Fields: Easier navigation due to fewer obstacles. Maintain a safe altitude and be mindful of wind conditions.
- Urban Areas: Requires more careful planning and attention to airspace restrictions. Avoid flying near buildings, power lines, and crowds.
Camera Operation and Image Capture
Capturing high-quality images and videos with a drone requires understanding camera settings and employing various filming techniques.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Adjusting ISO, shutter speed, and aperture are key to achieving optimal image quality. These settings interact to control exposure and image sharpness.
- ISO: Controls sensitivity to light. Higher ISO values are better for low-light conditions but can introduce noise.
- Shutter Speed: Controls the duration the camera’s sensor is exposed to light. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds blur motion.
- Aperture: Controls the amount of light entering the camera lens. A wider aperture (lower f-stop number) creates a shallower depth of field, blurring the background.
Drone Camera Shots and Angles
Drones offer a unique perspective for capturing various shots and angles.
- Overhead Shots: Provide a bird’s-eye view.
- Tracking Shots: Follow a moving subject.
- Low-Angle Shots: Create dramatic perspectives.
- Orbiting Shots: Circle a subject for a dynamic effect.
Capturing High-Quality Video Footage
Capturing smooth, high-quality video requires careful attention to camera settings and flight techniques. Maintaining a steady flight path and avoiding abrupt movements is crucial.
Stabilizing Footage and Minimizing Camera Shake

Most drones utilize gimbal stabilization to minimize camera shake. However, smooth flight techniques further enhance video quality. Avoid sudden movements and maintain a consistent speed and altitude.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting: How To Operate A Drone
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the longevity and performance of your drone. Knowing how to troubleshoot common problems can save time and money.
Drone Maintenance Schedule
| Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Clean drone body and propellers | After each flight |
| Inspect propellers for damage | Before each flight |
| Check battery voltage and charge level | Before each flight |
| Full drone inspection | Weekly |
| Battery deep discharge/charge cycle | Monthly |
Common Drone Malfunctions and Solutions, How to operate a drone
Several common issues can arise with drones. Understanding these and their solutions can prevent significant problems.
- Propeller damage: Replace damaged propellers.
- Low battery: Charge or replace the battery.
- GPS signal loss: Ensure clear skies and sufficient GPS signal strength.
- Gimbal malfunction: Recalibrate the gimbal or contact support.
Proper Battery Storage and Charging
Storing and charging drone batteries correctly extends their lifespan and ensures safety. Avoid extreme temperatures and follow manufacturer’s instructions.
Replacing Drone Components
Replacing components such as propellers and batteries is straightforward. Refer to the drone’s manual for specific instructions.
Advanced Drone Techniques
Advanced techniques allow for more complex and creative drone operations. Mastering these expands the possibilities for aerial photography and videography.
Waypoint and Automated Flight Planning
Waypoint systems allow you to pre-program a flight path, enabling automated drone operation. This is particularly useful for complex shots or repetitive tasks.
Performing Complex Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers such as orbiting and path following require practice and skill. These techniques create dynamic and engaging visual content.
Drone Flight Controllers

Different flight controllers offer varying capabilities, affecting flight performance and features. Factors to consider include processing power, sensor integration, and software support.
Utilizing Advanced Camera Features
Advanced camera features such as focus tracking and zoom control enhance the quality and creativity of your drone footage.
Mastering drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. This guide has provided a solid foundation, covering the essential steps from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Remember that consistent practice and adherence to safety regulations are paramount. As you gain experience, explore the limitless possibilities of aerial photography and videography, always prioritizing safety and responsible drone operation.
The skies await!
FAQ Insights
What type of drone is best for beginners?
User-friendly drones with GPS and automatic return-to-home features are ideal for beginners. Look for models with intuitive controls and obstacle avoidance systems.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model and flight conditions. Expect flight times ranging from 15 to 30 minutes, but always check your specific drone’s specifications.
What happens if I lose signal with my drone?
Most modern drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function that will automatically guide the drone back to its starting point if signal is lost. However, always remain vigilant and fly within visual line of sight.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by country and region. Check with your local aviation authority for specific regulations and registration procedures.
